- Let $r_1\text{ cm}$ and $r_2\text{ cm}$ be the base radii of the upper part and that of the middle part respectively.
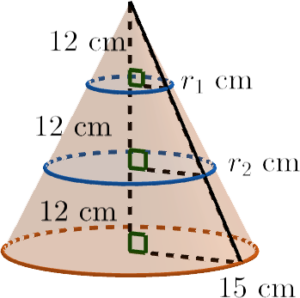
By the property of similar triangles, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{r_1}{15} & = & \dfrac{12}{36} \\
r_1 & = & 5
\end{array}$Also,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{r_2}{15} & = & \dfrac{24}{36} \\
r_2 & = & 10
\end{array}$Therefore, the volume of the middle part
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{3} \pi (10)^2 (24) – \dfrac{1}{3} \pi (5)^2 (12) \\
= & 700\pi\text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$ - Let $\ell_1\text{ cm}$ and $\ell_2\text{ cm}$ be the slant heights of the upper part and that of the middle part respectively.
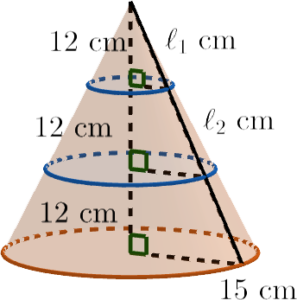
Consider the slant height of the upper part.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\ell_1^2 & = & 5^2 + 12^2 \\
\ell_1^2 & = & 169 \\
\ell_1 & = & 13 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Consider the slant height of of the middle part.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
(\ell_2 + 13)^2 & = & 10^2 + 24^2 \\
(\ell_2 + 13)^2 & = & 676 \\
\ell_2 + 13 & = & 26 \\
\ell_2 & = & 13
\end{array}$Therefore, the curved surface area of the middle part
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \pi (10) (26) – \pi (5) (13) \\
= & 195\pi \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
2020-I-12
Ans: (a) $700\pi\text{ cm}^3$ (b) $195\pi\text{ cm}^2$

