-
$\begin{array}{rcl}
g(x) & = & 3x^2+12kx+16k^2+8 \\
g(x) & = & 3(x^2 +4kx) +16k^2 +8 \\
g(x) & = & 3(x^2 +4kx +(2k)^2 -(2k)^2) +16k^2 +8 \\
g(x) & = & 3[(x+2k)^2 -4k^2] +16k^2 +8 \\
g(x) & = & 3(x+2k)^2 -12k^2 +16k^2 +8 \\
g(x) & = & 3(x+2k)^2 +4k^2 +8
\end{array}$Therefore, the coordinates of the vertex are $(-2k, 4k^2 +8)$.
- Sketch the graph according to the question. For sketching the graph, we assume $k=\dfrac{-3}{2}$.
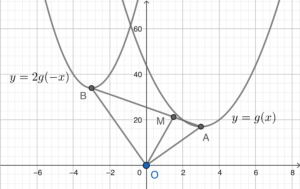
Note that the graph of $y=2g(-x)$ is obtained by first reflecting the graph of $y=g(x)$ along the $y$-axis, and then enlarging to $2$ times of the original along the $y$-axis.
Therefore, the coordinates of $B$ are $(2k, 8k^2+16)$.
Note also that $\Delta OBM$ and $\Delta OAM$ are triangles with the same height with respect to the base $BM$ and $AM$ respectively. Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{cl}
& AM : BM \\
= & \text{area of $\Delta OAM$} : \text{area of $\Delta OBM$} \\
= & 1 : 3
\end{array}$Hence, the coordinates of $M$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \left( \dfrac{3(-2k)+1(2k)}{3+1}, \dfrac{3(4k^2+8)+1(8k^2+16)}{3+1} \right) \\
= & \left(-k, \dfrac{20k^2+40}{4} \right) \\
= & (-k, 5k^2+10)
\end{array}$
2022-I-16
Ans: (a) $(-2k,4k^2+8)$ (b) $(-k,5k^2+10)$

