Denote the centre of the larger circle by $O$.
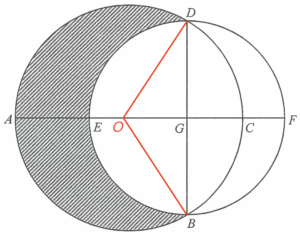
Since $AC$ is a diameter of the larger circle, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
2AO & = & AC \\
2AO & = & AG+CG \\
2AO & = & 30+10\\
AO & = & 20\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Note that $OA$ and $OC$ are radii of the larger circle, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
OC & = & OA \\
OG +CG & = & OA \\
OG +10 & = & 20 \\
OG & = & 10\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Since $EF$ and $BD$ are diameter of the smaller circle, then $G$ is the centre of the smaller circle. Hence, $DG$ and $BG$ are radii of the smaller circle.
Since $G$ is the mid-point of $BD$ and $O$ is the centre of the larger circle, then $\angle OGD= 90^\circ$ $\text{(line joining centre to the mid-point of chord $\perp$ chord)}$.
In $\Delta ODG$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
DG^2 & = & OD^2 -OG^2 \\
DG^2 & = & 20^2-10^2 \\
DG & = & \sqrt{300}\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Also,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\cos \angle DOG & = & \dfrac{OG}{OD} \\
\cos \angle DOG & = & \dfrac{10}{20} \\
\angle DOG & = & 60^\circ
\end{array}$
Note that $\Delta DGO \cong \Delta BGO$. Then $\angle BOG=\angle DOG$ and $\angle BOD =120^\circ$.
The area of the segment $BCD$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \text{area of the sector $OBCD$} -\text{area of $\Delta OBD$} \\
= & \pi (OB)^2 \dfrac{\angle BOD}{360^\circ} -\dfrac{1}{2} (BD) (OG) \\
= & \pi (20)^2 \dfrac{120^\circ}{360^\circ} -\dfrac{1}{2}\times 2\sqrt{300} \times 10 \\
= & 245.673\ 939\ 7\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
The area of the semi-circle $BEDG$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{2}\pi (BG)^2 \\
= & \dfrac{1}{2} \pi (\sqrt{300})^2 \\
= & 471.238\ 898 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
The area of the shaded region
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \pi (20)^2 -471.238\ 898-245.673\ 939\ 7 \\
= & 539.724\ 223\ 7\text{ cm}^2 \\
\approx & 540\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

