- Let $r\text{ cm}$ and $h\text{ cm}$ be the base radius and the height of $X$. According to the Figure 4(a), we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\overparen{ABC} & = & 2 \pi (20) \times \dfrac{216^\circ}{360^\circ} \\
& = & 240 \pi \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Note that the arc length is equal to the base circumference of $X$. Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
2\pi r & = & 24\pi \\
r & = & 12
\end{array}$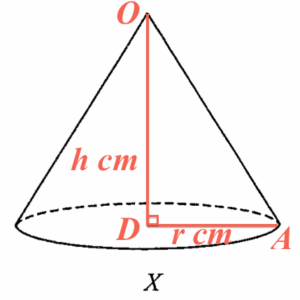
Refer to the above figure, by applying the Pythagoras Theorem to $\Delta OAD$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
OA^2 & = & OD^2 + DA^2 \\
20^2 & = & h^2 + 12^2 \\
h & = & \sqrt{400-144} \\
& = & 16
\end{array}$Therefore, the base radius and the height of $X$ are $12\text{ cm}$ and $16\text{ cm}$.
- The volume of $X$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{3} \times \pi (12)^2 \times 16 \\
= & 768\pi \text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$ - Let $y\text{ cm}$ be the base radius of $Y$. Then, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
2 \pi y & = & 2 \pi (10) \times \dfrac{108^\circ}{360^\circ} \\
y & = & 3
\end{array}$Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the base radius of }X}{\text{the base radius of }Y} & = & \dfrac{12}{3} \\
& = & 4
\end{array}$Also, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{OA}{PD} & = & \dfrac{20}{10} \\
& = & 2
\end{array}$Since the above two ratios are not equal, then $X$ and $Y$ are not similar.
2008-I-13
Ans: (a) Base radius $=12\text{ cm}$, height$=16\text{ cm}$ (b) $768\pi\text{ cm}^3$ (c) No

