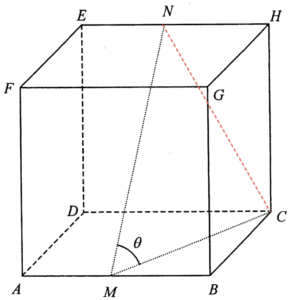
Join $NC$. Let $2x$ be the length of the cube, then $MB=x$. By applying the Pythagoras Theorem to $\Delta MBC$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
MC^2 & = & MB^2 + BC^2 \\
MC & = & \sqrt{x^2 + (2x)^2} \\
& = & \sqrt{5}x
\end{array}$
Note that $MC = NC$, then $NC = \sqrt{5}x$. By applying the Pythagoras Theorem to $\Delta BCH$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
HB^2 & = & BC^2 + HC^2 \\
HB & = & \sqrt{(2x)^2 + (2x)^2} \\
& = & \sqrt{8}x
\end{array}$
Note that $HB=NM$, then $NM = \sqrt{8}x$. By applying the cosine law to $\Delta MNC$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\cos \theta & = & \dfrac{MN^2 + MC^2 – NC^2}{2(MN)(MC)} \\
& = & \dfrac{(\sqrt{8}x)^2 + (\sqrt{5}x)^2 – (\sqrt{5}x)^2}{2(\sqrt{8}x)(\sqrt{5}x)} \\
& = & \dfrac{8}{2\sqrt{40}} \\
& = & \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& = & \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{10}} \times \dfrac{\sqrt{10}}{\sqrt{10}} \\
& = & \dfrac{\sqrt{10}}{5}
\end{array}$

