-
- By cosine law, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
BC^2 & = & AB^2 + AC^2 -2(AB)(AC)\cos \angle BAC \\
& = & 20^2 + 30^2 -2(20)(30)\cos 56^\circ \\
& = & 628.968~515~8 \\
BC & = & 25.079~244~72 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$ - By sine law, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{AB}{\sin \angle ACB} & = & \dfrac{BC}{\sin \angle BAC} \\
\dfrac{20}{\sin \angle ACB} & = & \dfrac{25.079~244~72}{\sin 56^\circ} \\
\sin \angle ACB & = & \dfrac{20\sin56^\circ}{25.079~244~72} \\
\sin \angle ACB & = & 0.661~134~401 \\
\angle ACB & = & 41.386~446~19^\circ
\end{array}$ - Add points $X$ and $Y$ on $DE$ and $BC$ respectively such that $AX \perp DE$ and $AY\perp BC$.
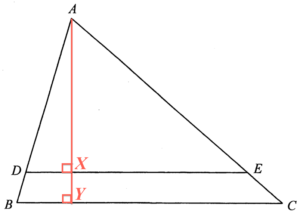
Consider $\Delta AYC$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle ACY & = & \dfrac{AY}{AC} \\
\sin 41.386~446~19^\circ & = & \dfrac{AY}{30} \\
AY & = & 30 \sin 41.386~446~19^\circ \\
& = & 19.834~032~05 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Then, the perpendicular distance from $A$ to $DE$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 19.834~032~05 – 4 \\
= & 15.834~032~05\text{ cm}
\end{array}$ - Note that $\Delta ABC \sim \Delta ADE$.
Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{AX}{AY} & = & \dfrac{DE}{BC} \\
\dfrac{15.834~032~05}{19.834~032~05} & = & \dfrac{DE}{25.079~244~72} \\
DE & = & 20.021~423~97\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
- By cosine law, we have
-
- Add a point $X$ on $DE$ such that $AX\perp DE$ and $PX\perp DE$. Note that this point $X$ is the same as that in (a).
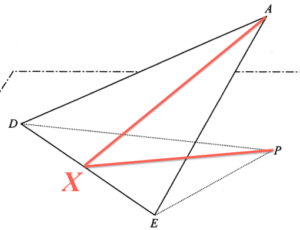
Consider $\Delta PDE$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{1}{2} (PX)(DE) & = & 120 \\
\dfrac{1}{2} (PX)(20.021~423~97) & = & 120 \\
PX & = & 11.987~159~37 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Since $P$ is the projection of $A$ on the horizontal ground, then $\angle APX = 90^\circ$ and $\Delta APX$ is a right-angled triangle. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\cos \angle AXP & = & \dfrac{PX}{AX} \\
& = & \dfrac{11.987~159~37}{15.834~032~05} \\
& = & 0.757~050~341 \\
\angle AXP & = & 40.795~151~95^\circ
\end{array}$Therefore, the required angle is $52.816~241~61^\circ$.
- Note that the shortest distance from $A$ to the horizontal ground is $AP$, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle AXP & = & \dfrac{AP}{AX} \\
\sin 40.795~151~95^\circ & = & \dfrac{AP}{15.834~032~05} \\
AP & = & 10.345~268~53\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
- Add a point $X$ on $DE$ such that $AX\perp DE$ and $PX\perp DE$. Note that this point $X$ is the same as that in (a).
2011-I-17
Ans: (a) (i) $25.1\text{ cm}$ (ii) $41.4^\circ$ (iii) $15.8\text{ cm}$ (iv) $20.0\text{ cm}$ (b) (i) $40.8^\circ$ (ii) $10.3\text{ cm}$

