In $\Delta ATC$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle TAC & = & 180^\circ-90^\circ-20^\circ \\
& = & 70^\circ
\end{array}$
Join $AB$.
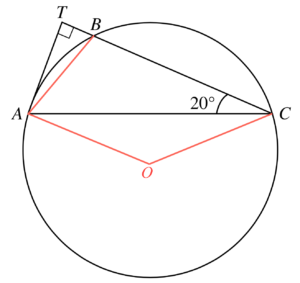
$\angle BAT = \angle ACB = 20^\circ$.
In $\Delta ABC$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle BAC & = & 70^\circ -20^\circ \\
& = & 50^\circ
\end{array}$
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle ABC & = & 180^\circ – 50^\circ-20^\circ \\
& = & 110^\circ
\end{array}$
By sine law, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{AC}{\sin 110^\circ} & = & \dfrac{BC}{\sin 50^\circ} \\
AC & = & \dfrac{6 \sin 110^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ} \\
& = & 7.360~089~581\mbox{ cm}
\end{array}$
Denote $O$ as the centre of the circle. Join $OA$ and $OC$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\mbox{reflex }\angle AOC & = & 2\times \angle ABC \\
& = & 2\times 110^\circ \\
& = & 220^\circ
\end{array}$
In $\Delta OAC$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle AOC & = & 360^\circ – 220^\circ \\
& = & 140^\circ
\end{array}$
Let $r\mbox{ cm}$ be the radius of the circle. By cosine law, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
AC^2 & = & OA^2 +OC^2 -2(OA)(OC) \cos \angle AOC \\
(\dfrac{6\sin110^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ})^2 & = & r^2+r^2-2r^2\cos 140^\circ \\
(\dfrac{6\sin110^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ})^2 & = & r^2(2-2\cos140^\circ) \\
r^2 & = & (\dfrac{6\sin110^\circ}{\sin 50^\circ})^2 \times \dfrac{1}{2-2\cos 140^\circ} \\
r^2 & = & 15.336~793~72 \\
r & = & 3.916~221~868 \\
\end{array}$
Therefore, the radius is $3.9\mbox{ cm}$ correct to the nearest $0.1\mbox{ cm}$.

