Join $AE$.
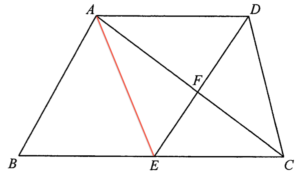
Since $AD:BC=2:3$ and $E$ is the mid-point of $BC$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
AD:EC & = & 2:\dfrac{3}{2} \\
& = & 4:3
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta ADF \sim \Delta CEF$, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of }\Delta ADF}{\text{the area of }\Delta CEF} & = & \left(\dfrac{AD}{CE}\right)^2 \\
\text{the area of }\Delta ADF & = & 36 \times \left(\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2 \\
& = & 64\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta CFD$ and $\Delta CEF$ have the same height, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of }\Delta CFD}{\text{the area of }\Delta CEF} & = & \dfrac{DF}{EF} \\
& = & \dfrac{AD}{CE} \\
\text{the area of }\Delta CFD & = & 36 \times \dfrac{4}{3} \\
& = & 48\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta AEF$ and $\Delta CEF$ have the same height, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of }\Delta AEF}{\text{the area of }\Delta CEF} & = & \dfrac{AF}{CF} \\
& = & \dfrac{AD}{CE} \\
\text{the area of }\Delta CFD & = & 36 \times \dfrac{4}{3} \\
& = & 48\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta ABE$ and $\Delta ACE$ have the same height, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of }\Delta ABE}{\text{the area of }\Delta ACE} & = & \dfrac{BE}{CE} \\
\text{the area of }\Delta CFD & = & 36 + 48 \\
& = & 84\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Therefore, the area of the trapezium $ABCD$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 64+48+36+48+84 \\
= & 280\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

