- By applying sine law to $\Delta VAB$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{AB}{\sin \angle AVB} & = & \dfrac{VB}{\sin \angle VAB} \\
\dfrac{18}{\sin \angle AVB} & = & \dfrac{30}{\sin \angle 110^\circ} \\
\sin \angle AVB & = & \dfrac{18\sin 110^\circ}{30} \\
\angle AVB & = & 34.320\ 082\ 91^\circ
\end{array}$Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle VBA & = & 180^\circ – \angle AVB – \angle VAB \\
& = & 35.679\ 917\ 09^\circ \\
& \approx & 35.7^\circ
\end{array}$ - Since $P$ and $M$ are mid-points of $AB$ and $VB$ respectively, then $BP=9\text{ cm}$ and $BM=15\text{ cm}$. By applying cosine law to $\Delta BMP$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
MP^2 & = & BP^2 + BM^2 -2(BP)(BM)\cos \angle VBA \\
MP^2 & = & 86.682\ 235\ 75 \\
MP & = & 9.310\ 329\ 519 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Since $M$ and $N$ are mid-points of $VB$ and $VC$ respectively, then by applying the Mid-point Theorem to $\Delta VBC$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
MN & = & \dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \\
& = & 5 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Since $P$ and $Q$ are mid-points of $AB$ and $DC$ respectively, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
PQ & = & BC \\
& = & 10 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Consider the trapezium $PQNM$. Let $h \text{ cm}$ be the height of the trapezium $PQNM$.
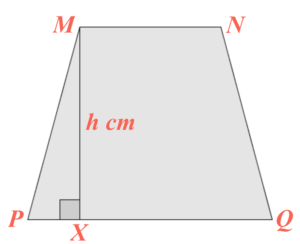
Note that $MP=NQ$. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
PX & = & \dfrac{PQ-MN}{2} \\
& = & 2.5\text{ cm}
\end{array}$Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
h & = & \sqrt{MP^2 – PX^2} \\
& = & 8.968\ 402\ 073 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Hence, the area of the trapezium $PQNM$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{2} (MN+PQ)\times h \\
= & \dfrac{1}{2} ( 10+ 5 ) \times 8.968\ 402\ 073\\
= & 67.263\ 015\ 55 \text{ cm}^2 \\
< & 70 \text{ cm}^2 \end{array}$Therefore, I agree with the craftsman.
2014-I-17
Ans: (a) $35.7^\circ$ (b) Yes

