- The total volume of the two pyramids
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \text{the volume of the prism} \\
= & 84 \times 20 \\
= & 1\ 680 \text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$Since the two solid right pyramids are similar, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the volume of the smaller pyramid}}{\text{the volume of the larger pyramid}} & = & \left(\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{9}} \right)^3 \\
& = & \dfrac{8}{27}
\end{array}$Hence, the volume of the larger pyramid
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 1\ 680 \times \dfrac{27}{27+8} \\
= & 1\ 296 \text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$ - Below shows the figure of the larger pyramid.
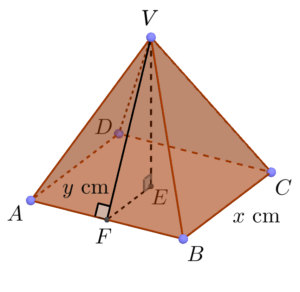
Note that $VE$ is the height of the pyramid, then $E$ is the foot of perpendicular of $V$. Note also that $VF$ be the height of the $\Delta VAB$.
Let $x\text{ cm}$ be the length of the base of the larger pyramid. By the result of (a), we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{1}{3} \times x^2 \times 12 & = & 1\ 296 \\
x & = & 18
\end{array}$Let $y\text{ cm}$ be the length of $VF$. Consider the $\Delta VEF$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcll}
VF^2 & = & FE^2 + VE^2 & \text{(Pyth. Thm.)} \\
y^2 & = & 9^2 + 12^2 & \\
y & = & \sqrt{225} & \\
y & = & 15
\end{array}$Therefore, the area of $\Delta VAB$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{2} \times 18 \times 15 \\
= & 135 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$Therefore, the total surface area of the larger pyramid
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 4 \times 135 + 18^2 \\
= & 864 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the total surface area of the smaller pyramid}}{\text{the total surface area of the larger pyramid}} & = & \dfrac{4}{9} \\
\dfrac{\text{the total surface area of the smaller pyramid}}{864} & = & \dfrac{4}{9} \\
\text{the total surface area of the smaller pyramid} & = & 384 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
2017-I-12
Ans: (a) $1296\text{ cm}^3$ (b) $384\text{ cm}^2$

