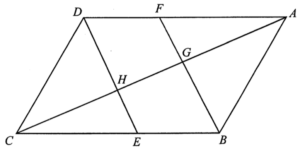
Since $\Delta CEH \sim \Delta CBG$, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{CE}{CB} & = & \dfrac{EH}{BG} \\
\dfrac{CE}{CE + EB} & = & \dfrac{EH}{BG} \\
\dfrac{3}{3 + 2} & = & \dfrac{EH}{BG} \\
BG : EH & = & 5 : 3
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta CEH \cong \Delta AFG$, then $EH = FG$. Hence, we have $BG:FG = 5:3$.
Since $\Delta AFG$ and $\Delta ABG$ have the same height with respect to the bases $FG$ and $BG$ respectively, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{Area of }\Delta AFG}{\text{Area of }\Delta ABG} & = & \dfrac{FG}{BG} \\
\dfrac{\text{Area of }\Delta AFG}{135} & = & \dfrac{3}{5} \\
\text{Area of }\Delta AFG & = & 81 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta ABG \cong \Delta CDH$, then the area of $\Delta CDH = 135\text{ cm}^2$.
Since $\Delta CEH \sim \Delta CBG$ and $BG:EH=5:3$, then $CG: CH = 5 : 3$. Hence, $CH:HG = 3:2$.
Since $\Delta CEH \cong \Delta AFG$, then $CH = AG$. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{cl}
& CH : CA \\
= & CH : (CH + HG + GA) \\
= & 3 : 8
\end{array}$
Since $\Delta CDH$ and $\Delta CDA$ have the same height with respect to the bases $CH$ and $CA$ respectively, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{Area of }\Delta CDH}{\text{Area of }\Delta CDA} & = & \dfrac{CH}{CA} \\
\dfrac{135}{\text{Area of }\Delta CDA} & = & \dfrac{3}{8} \\
\text{Area of }\Delta CDA & = & 360 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Therefore, the area of the quadrilateral $DFGH$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \text{Area of }\Delta CDA – \text{Area of }\Delta CDH – \text{Area of }\Delta AFG \\
= & 360 – 135 – 81 \\
= & 144 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

