- Let $f(x) = k_1 x^2 + k_2x$, where $k_1$ and $k_2$ are non-zero constants.For $f(2) = 60$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
k_1 (2)^2 + k_2(2) & = & 60 \\
2k_1 + k_2 & = & 30 \ \ldots \unicode{x2460}
\end{array}$For $f(3) = 99$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
k_1(3)^2 + k_2(3) & = & 99 \\
3k_1 + k_2 & = & 33 \ \ldots \unicode{x2461}
\end{array}$$\unicode{x2461} – \unicode{x2460}$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
k_1 & = & 3
\end{array}$Sub. $k_1 = 3$ into $\unicode{x2460}$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
2(3) + k_2 & = & 30 \\
k_2 & = & 24
\end{array}$Therefore, $f(x) = 3x^2 + 24x$.
-
- By the result of (a), we have$\begin{array}{rcl}
f(x) & = & 3x^2 + 24x \\
& = & 3(x^2 + 8x) \\
& = & 3\left[x^2 + 8x + \left(\dfrac{8}{2}\right)^2 – \left(\dfrac{8}{2}\right)^2\right] \\
& = & 3(x + 4)^2 – 48
\end{array}$Therefore, the coordinates of $Q$ are $(-4, -48)$.
- Note that $y= 27 – f(x)$ means $f(x)$ is reflected about $x$ axis and then translated upwards by $27$ units. Then the $x$ coordinate of $Q$ and $R$ are the same, the $y$ coordinate of $R$$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 27 – \text{the $y$ coordinate of $Q$} \\
= & 27 – (-48) \\
= & 75
\end{array}$Therefore, the coordinates of $R$ are $(-4, 75)$.
- Sketch the graph below according to the information of the question.
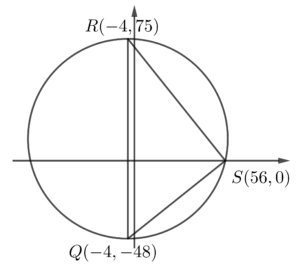
Consider $\Delta QRS$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
RS^2 + QS^2 & = & (56-(-4)^2 + (0-75)^2 + (56-(-4))^2 + (0-(-48))^2 \\
& = & 15129
\end{array}$Also,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
RQ^2 & = & (75-(-48))^2 \\
& = & 15129
\end{array}$Since $RS^2 + QS^2 = RQ^2$, then by the converse of the Pythagoras Theorem, $\Delta QRS$ is a right-angled triangle with $\angle QSR =90^\circ$.
Since $\angle QSR = 90^\circ$, then by the converse of $\angle$ in the semi-circle, $QR$ is a diameter of the circle.
Since $P$ is the circumcentre of $\Delta QRS$, then $P$ is the mid-point of $QR$.
- By the result of (a), we have$\begin{array}{rcl}
2018-I-18
Ans: (a) $f(x) = 3x^2 + 24x$ (b) (i) $(-4, -48)$ (ii) $(-4, 75)$ (iii) $P$ is the mid-point of $QR$.

