Since $OC \perp AD$, then $AE = DE$. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
DE & = & \dfrac{1}{2} AD \\
DE & = & \dfrac{1}{2} ( AF + FD) \\
DE & = & \dfrac{1}{2}(9 + 39) \\
DE & = & 24 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$
By applying the Pythagoras Theorem to $\Delta CDE$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
OD^2 & = & OE^2 + DE^2 \\
OD^2 & = & 18^2 + 24^2 \\
OD & = & 30 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Add point $G$ on $OC$ such that $OC \perp BG$.
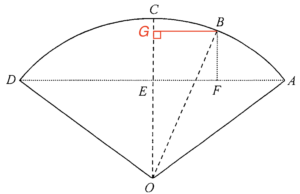
Note that $BFEG$ is a rectangle. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
BG & = & FE \\
BG & = & AE – AF \\
BG & = & DE – AF \\
BG & = & 24 – 9 \\
BG & = & 15\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta OBG$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle BOG & = & \dfrac{BG}{OB} \\
\sin \angle BOG & = & \dfrac{BG}{OD} \\
\sin \angle BOG & = & \dfrac{15}{30} \\
\angle BOG & = & 30^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, the area of the sector $OBC$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \pi \times 30^2 \times \dfrac{30^\circ}{360^\circ} \\
= & 75\pi \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

