Ans: (a) $(k, k^2 + 4)$ (b) No
-
$\begin{array}{rcl}
g(x) & = & x^2 -2kx +2k^2 +4 \\
& = & x^2 -2kx +k^2 +k^2 +4 \\
& = & (x -k)^2 +k^2 +4
\end{array}$Therefore, the vertex of the graph of $y = g(x)$ is $(k, k^2 + 4)$.
- We sketch the graphs of $y=g(x)$, $y=g(x+2)$ and $y=-g(x-2)$ as shown.
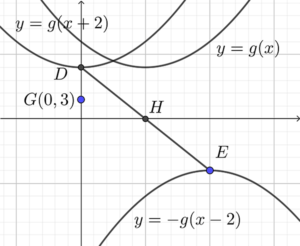
Note that the coordinates of $D$ and $E$ are $(k -2,k^2 +4)$ and $(k+2, -k^2 -4)$ respectively.
For the circumcircle of $\Delta DEF$, $DE$ is a chord of the circle. Hence, the perpendicular bisector of $DE$ must pass through the circumcentre of $\Delta DEF$. Let $H$ be the mid-point of $DE$ and $G=(0,3)$.
The slope of $DE$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{(k^2 + 4) -(-k^2 -4)}{(k-2) -(k+2)} \\
= & \dfrac{-(k^2 + 4)}{2}
\end{array}$The coordinates of $H$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \left(\dfrac{(k-2) +(k+2)}{2}, \dfrac{(k^2 +4) + (-k^2 -4)}{2} \right) \\
= & (k, 0)
\end{array}$The slope of $GH$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{0- 3}{k -0} \\
= & \dfrac{-3}{k}
\end{array}$Since $GH \perp DE$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{-3}{k} \times \dfrac{-(k^2 +4)}{2} & = & -1 \\
3k^2 +12 & = & -2k \\
3k^2 +2k +12 & = & 0
\end{array}$Consider the discriminant of $3k^2 +2k +12 =0$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\Delta & = & (2)^2 -4(3)(12) \\
& = & -140 \\
& < & 0
\end{array}$Therefore, the equation $3k^2 +2k +12 = 0$ has no real roots.
Therefore, there is no point $F$ on the same rectangular coordinate system such that the coordinates of the cricumcentre of $\Delta DEF$ are $(0,3)$.

