- Join $PR$.
By applying sine law to $\Delta PQR$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{PR}{\sin \angle PQR} & = & \dfrac{PQ}{\sin \angle PRQ} \\
\dfrac{PR}{\sin 30^\circ} & = & \dfrac{60}{\sin 55^\circ} \\
PR & = & 36.623\ 237\ 66^\circ
\end{array}$Also,
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle QPR & = & 180^\circ – 30^\circ – 55^\circ & \text{($\angle$ sum of $\Delta$)} \\
\angle QPR & = & 95^\circ
\end{array}$By applying cosine law to $\Delta PRS$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
RS^2 & = & PS^2 + PR^2 – 2\times PS \times PR \times \cos \angle RPS \\
RS^2 & = & 40^2 + 36.623\ 237\ 66^2 – 2 \times 40 \times 36.623\ 237\ 66 \times \cos (120^\circ – 95^\circ) \\
RS & = & 16.908\ 799\ 44\text{ cm}
\end{array}$ - The area of the paper card
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{2} \times PQ \times PR \times \sin \angle QPR + \dfrac{1}{2} \times PR \times PS \times \sin \angle RPS \\
= & \dfrac{1}{2} \times 60 \times 36.623\ 237\ 66 \times \sin 95^\circ + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 36.623\ 237\ 66 \times 40 \times \sin 25^\circ \\
= & 1404.069\ 236 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$ -
- Let $P’$ be the projection of $P$ on the horizontal ground and $M$ be the foot of the perpendicular from $P$ to $QR$.
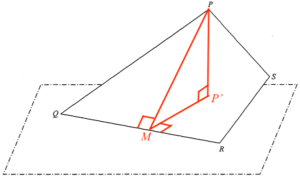
Consider $\Delta PMQ$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle PQM & = & \dfrac{PM}{PQ} \\
\sin 30^\circ & = & \dfrac{PM}{60} \\
PM & = & 30\text{ cm}
\end{array}$Since the angle between the paper card and the horizontal ground is $32^\circ$, then $\angle PMP’ = 32^\circ$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle PMP’ & = & \dfrac{PP’}{PM} \\
\sin 32^\circ & = & \dfrac{PP’}{30} \\
PP’ & = & 15.897\ 577\ 93 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Therefore, the shortest distance from $P$ to the horizontal ground is $15.9\text{ cm}$.
- Let $S’$ be the projection of $S$ on the horizontal ground and $N$ be the intersection of $PS$ produced and $P’S’$ produced.
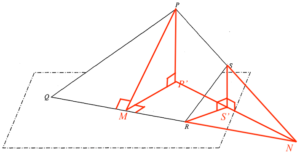
Consider $\Delta PQN$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle PNQ & = & 180^\circ – 30^\circ – 120^\circ & \text{($\angle$ sum of $\Delta$)} \\
\angle PNQ & = & 30^\circ \\
\therefore PQ & = & PN & \text{(base $\angle$s, isos. $\Delta$)}
\end{array}$Note that $\Delta PNP’ \sim SNS’$. Then we have
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\dfrac{SS’}{PP’} & = & \dfrac{SN}{PN} & \text{(corr. sides, $\sim \Delta$s)} \\
\dfrac{SS’}{PP’} & = & \dfrac{PN – PS}{PN} \\
\dfrac{SS’}{15.897\ 577\ 93} & = & \dfrac{60 – 40}{60} \\
SS’ & = & 5.299\ 192\ 642 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$Note that the angle between $RS$ and the horizontal ground is $\angle SRS’$. Consider $\Delta SRS’$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin \angle SRS’ & = & \dfrac{SS’}{RS} \\
\sin \angle SRS’ & = & \dfrac{5.299\ 192\ 642}{16.908\ 799\ 44} \\
\angle SRS’ & = & 18.264\ 160\ 68^\circ \\
\angle SRS’ & \le & 20^\circ
\end{array}$Therefore, the claim is correct.
- Let $P’$ be the projection of $P$ on the horizontal ground and $M$ be the foot of the perpendicular from $P$ to $QR$.
2020-I-19
Ans: (a) $16.9\text{ cm}$ (b) $1400\text{ cm}^2$ (c) (i) $15.9\text{ cm}$ (ii) Yes

