Join $DG$.
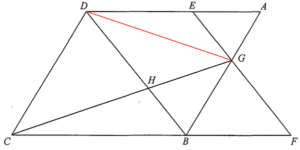
Consider $\Delta AEG$ and $\Delta DEG$. Since their heights are the same with bases $AE$ and $DE$ respectively, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta DEG$}}{\text{the area of $\Delta AEG$}} & = & \dfrac{DE}{AE} \\
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta DEG$}}{48} & = & \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\text{the area of $\Delta DEG$} & = & 120 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $BF = DE$ and $AD//CF$, then $BFED$ is a parallelogram. Hence, we have $EG//DB$.
Since $EG//DB$, then $\Delta AEG \sim \Delta ADB$. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
AG : GB & = & AE : ED \\
AG : GB & = & 2 : 5
\end{array}$
Since $ABCD$ is a parallelogram, then $AB = DC$. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
AG : GB : DC & = & AG : GB : AB \\
AG : GB : DC & = & 2 : 5 : 7
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta ADG$ and $\Delta CDG$. Since their heights are the same with bases $AG$ and $CD$ respectively. Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta CDG$}}{\text{the area of $\Delta ADG$}} & = & \dfrac{CD}{AG} \\
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta DEG$}}{48 + 120} & = & \dfrac{7}{2} \\
\text{the area of $\Delta DEG$} & = & 588 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$
Since $ABCD$ is a parallelogram, then $AB // DC$. Hence, we have $\Delta BGH \sim \Delta DCH$. Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{CH}{GH} & = & \dfrac{CG}{GB} \\
\dfrac{CH}{GH} & = & \dfrac{7}{5}
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta CDH$ and $\Delta DGH$. Since their heights are the same with bases $CH$ and $GH$ respectively, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta CDH$}}{\text{the area of $\Delta DGH$}} & = & \dfrac{CH}{GH} \\
\dfrac{\text{the area of $\Delta CDH$}}{\text{the area of $\Delta DGH$}} & = & \dfrac{7}{5}
\end{array}$
Hence, the area of $\Delta CDH$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \text{the area of $\Delta CDG$} \times \dfrac{7}{7 + 5} \\
= & 588 \times \dfrac{7}{12} \\
= & 343 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

