In $\Delta BCE$,
$\begin{array}{cl}
& BE^2 + BC^2 \\
= & 8^2 + 15^2 \\
= &289
\end{array}$
Also,
$\begin{array}{cl}
& BC^2 \\
= & 17^2 \\
= & 289
\end{array}$
Since $BE^2 + CE^2 = BC^2$, then by converse of Pythagoras Theorem, $\Delta BCE$ is a right-angled triangle with $\angle BEC = 90^\circ$.
Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\cos \angle EBC & = & \dfrac{BE}{BC} \\
\cos \angle EBC & = & \dfrac{8}{17} \\
\angle EBC & = & 61.927\ 513\ 06^\circ
\end{array}$
Add a point $F$ on $BC$ such that $EF \perp BC$.
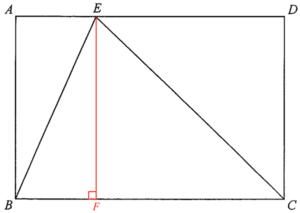
Consider $\Delta BEF$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\sin angle EBF & = & \dfrac{EF}{BE} \\
EF & = & 8 \times \sin 61.927\ 513\ 06^\circ \\
EF & = & 7.058\ 823\ 529 \text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the area of the rectangle $ABCD$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & BC \times EF \\
= & 17 \times 7.058\ 823\ 529 \\
= & 120 \text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$

