Add a point $F$ on the circle $CDE$. Join $DF$ and $EF$.
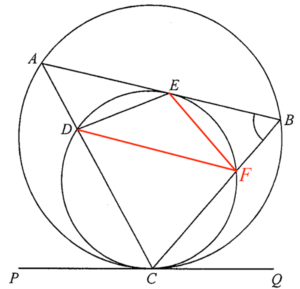
Consider $\Delta CDF$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle CDF & = & \angle BCQ & \text{($\angle$ in alt. segment)} \\
\angle CDF & = & 35^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle ADE + \angle EDF + \angle CDF & = & 180^\circ & \text{(adj. $\angle$s on a st. line)} \\
100^\circ + \angle EDF + 35^\circ & = & 180^\circ \\
\angle EDF & = & 45^\circ
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta ABC$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle BAC & = & \angle BCQ & \text{($\angle$ in alt. segment)} \\
\angle BAC & = & 35^\circ
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta ADE$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle ADE + \angle AED + \angle DAE & = & 180^\circ & \text{($\angle$ sum of $\Delta$)} \\
100^\circ + \angle AED + 35^\circ & = & 180^\circ \\
\angle AED & = & 45^\circ
\end{array}$
Consider $\Delta DEF$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle DFE & = & \angle AED & \text{($\angle$ in alt. segment)} \\
\angle DFE & = & 45^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle DEF + \angle EDF + \angle EFD & = & 180^\circ & \text{($\angle$ sum of $\Delta$)} \\
\angle DEF + 45^\circ + 45^\circ & = & 180^\circ \\
\angle DEF & = & 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Consider quadrilateral $CDEF$.
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle DCF + \angle DEF & = & 180^\circ & \text{(opp. $\angle$s, cyc. quad.)} \\
\angle DCF + 90^\circ & = & 180^\circ \\
\angle DCF & = & 90^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, consider $\Delta ABC$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcll}
\angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC & = & 180^\circ & \text{($\angle$ sum of $\Delta$)} \\
\angle ABC + 90^\circ + 35^\circ & = & 180^\circ \\
\angle ABC & = & 55^\circ
\end{array}$

