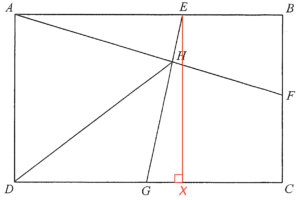
Add a point $X$ on $CD$ such that $EX \perp CD$. Hence, $EX=BC= 597\text{ cm}$ and
$\begin{array}{rcl}
CX & = & EB \\
CX & = & AB-AE \\
CX & = & 960-638 \\
CX & = & 322\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
Therefore, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
GX & = & GC -CX \\
GX & = & 480 -322 \\
GX & = & 158\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
In $\Delta EGX$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\tan \angle EGX & = & \dfrac{EX}{GX} \\
\tan \angle EGX & = & \dfrac{597}{158} \\
\angle EGX & = & 75.176\ 157\ 96^\circ
\end{array}$
Since $AB\text{//} DC$, $\angle AEG = \angle EGX = 75.176\ 157\ 96^\circ$.
In $\Delta ABF$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\tan \angle BAF & = & \dfrac{BF}{AB} \\
\tan \angle BAF & = & \dfrac{280}{960} \\
\angle BAF & = & 16.260\ 204\ 71^\circ
\end{array}$
In $\Delta AEH$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{AE}{\sin \angle AHE} & = & \dfrac{AH}{\sin \angle AEH} \\
\dfrac{638}{\sin (180^\circ-75.176\ 157\ 96^\circ -16.260\ 204\ 71^\circ)} & = & \dfrac{AH}{\sin 75.176\ 157\ 96^\circ} \\
AH & = & 616.959\ 310\ 6\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
In $\Delta ADH$,
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\angle DAH & = & 90^\circ- \angle BAF \\
\angle DAH & = & 90^\circ -16.260\ 204\ 71^\circ \\
\angle DAH & = & 73.739\ 795\ 29^\circ
\end{array}$
Hence, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
DH^2 & = & AD^2 +AH^2 -2(AD)(AH)\cos \angle DAH \\
DH^2 & = & 597^2 +(616.959\ 310\ 6)^2 -2(597)(616.959\ 310\ 6)\cos 73.739\ 795\ 29^\circ\\
DH & = & 728.550\ 584\ 5 \\
DH & \approx & 728\text{ cm}
\end{array}$

