This is out of syllabus after 2022.
-
$\begin{array}{rcl}
y & = & e^{2x-6} \\
\dfrac{dy}{dx} & = & 2e^{2x-6}
\end{array}$The slope of the tangent at $x=3$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|_{x=3} \\
= & 2e^{2(3)-6} \\
= & 2
\end{array}$Hence, the slope of $L$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & -1\div \left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|_{x=3} \\
= & -1 \div 2 \\
= & \dfrac{-1}{2}
\end{array}$By the point slope form, the equation of $L$ is
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{y-1}{x-3} & = & \dfrac{-1}{2} \\
2y-2 & = & -x +3 \\
x+2y-5 & = & 0
\end{array}$Sub. $x=c$ and $y=0$ into the equation of $L$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
c+2(0)-5 & = & 0 \\
c & = & 5
\end{array}$ - Sketch a graph according to the question.
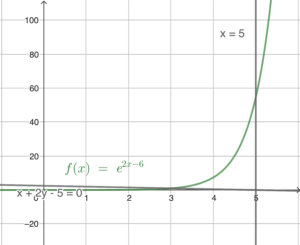
Rewrite the equation of $L$ to slope intercept form, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
x+2y-5 & = & 0 \\
2y & = & -x+5 \\
y & = & \dfrac{-1}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}
\end{array}$The required area
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dint_3^5 \left(e^{2x-6}-\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\right) dx \\
= & \dint_3^5\left(e^{2x-6}+\dfrac{1}{2}x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right) dx \\
= & \left[\dfrac{e^{2x-6}}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}x^2-\dfrac{5}{2}x\right]_3^5 \\
= & \dfrac{e^2(5)-6}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}(5)^2-\dfrac{5}{2}(5)-\dfrac{e^{2(3)-6}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}(3)^2+\dfrac{5}{2}(3) \\
= & \dfrac{e^4-3}{2}
\end{array}$

