- The equation of the straight line passing through $A$ and $G$ is
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{y-112}{x-83} & = & \dfrac{12-112}{158-83} \\
3y-336 & = & -4x+332 \\
4x+3y -668 & = & 0
\end{array}$ - Sketch the graph according to the question.
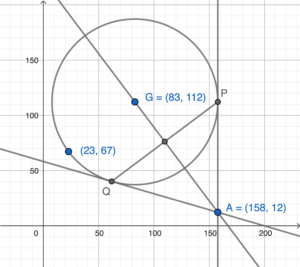
Without loss of generality, let $P$ be the intersection point just above the point $A$.
The radius of $C$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \sqrt{(83-23)^2 +(112-67)^2} \\
= & 75
\end{array}$Note that $AP$ is a vertical line, then $GP$ is a horizontal line. Then the coordinates of $P$ are $(158,112)$.
Since $AG\perp PQ$, then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
m_{PQ} \times m_{AG} & = & -1 \\
m_{PQ} \times \dfrac{-4}{3} & = & -1 \\
m_{PQ} & = & \dfrac{3}{4}
\end{array}$Therefore, the equation of the straight line passing through $P$ and $Q$ is
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{y-112}{x-158} & = & \dfrac{3}{4} \\
4y-448 & = & 3x-474 \\
3x-4y-26 & = & 0
\end{array}$For the intersection point of $AG$ and $PQ$,
$\left\{ \begin{array}{ll}
4x+3y-668=0 & \ldots \unicode{x2460} \\
3x-4y-26=0 & \ldots \unicode{x2461}
\end{array}\right.$$4\times \unicode{x2460} +3 \times \unicode{x2461}$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
25x -2750 & = & 0 \\
x & = & 110
\end{array}$Sub. $x=110$ into $\unicode{x2460}$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
4(110)+3y-668 & = & 0 \\
y & = & 76
\end{array}$Therefore, the coordinates of the intersection point are $(110, 76)$.
- Let $I$ and $r$ be the in-centre and the radius of the inscribed circle of $\Delta APQ$ respectively.
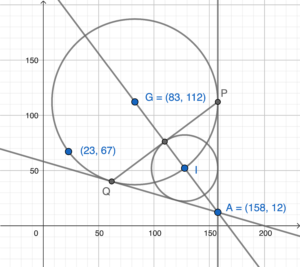
Note that the $x$-coordinate of $I$ is $158-r$. Note also that $I$ lies on $AG$. Then sub. $x=158-r$ into $4x+3y-668=0$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
4(158-r)+3y-668 & = & 0 \\
632-4r+3y-668 & = & 0 \\
3y & = & 4r+36 \\
y & = & \dfrac{4r+36}{3}
\end{array}$Therefore, $I=\left(158-r, \dfrac{4r+36}{3}\right)$.
Consider the radius of the inscribed circle of $\Delta APQ$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
((158-r)-110)^2 +\left(\dfrac{4r+36}{3} -76\right)^2 & = & r^2 \\
(48-r)^2 + \left( \dfrac{4r-192}{3}\right)^2 & = & r^2 \\
20736 -864r +9r^2 +16r^2-1536r+36864 -r^2 & = & 0 \\
16r^2-2400r +57600 & = & 0 \\
r^2 -150r +3600 & = & 0 \\
(r-30)(r-120) & = & 0
\end{array}$$\therefore r=30$ or $r=120$ (rejected).
Therefore, $I=(128,52)$.
Hence, the equation of the inscribed circle is $(x-128)^2+(y-52)^2=900$.
- Since $\angle APG = \angle AQG =90^\circ$, then $\angle APG + \angle AQG = 180^\circ$. Therefore, $A$, $P$, $G$ and $Q$ are concyclic.
Hence, the circle passes through $A$, $P$, $G$ and $Q$ is the circumcircle of $\Delta APQ$.
Since $\angle APG =90^\circ$, then $AG$ is a diameter of the circumcircle.
Since all circles are similar, then we have
$\begin{array}{cl}
& \text{the area of the inscribed circle} : \text{the area of the circumcircle} \\
= & (\text{radius of the inscribed circle})^2 : (\text{radius of the circumcircle})^2 \\
= & 30^2 : \left(\dfrac{AG}{2}\right)^2 \\
= & 900 : \dfrac{1}{4}[(83-158)^2+(112-12)^2] \\
= & 900 : 3906.25 \\
= & 144 : 624 \\
\neq & 1:4
\end{array}$Therefore, the claim is not agreed.
2022-I-19
Ans: (a) $4x+3y-668=0$ (b) $(110,76)$ (c) $(x-128)^2+(y-52)^2=900$ (d) No

