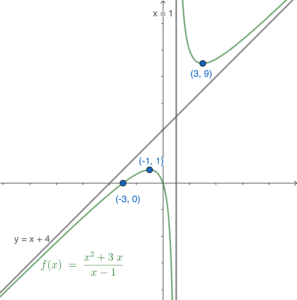
- Since $f(x)$ is undefined at $x=1$. Therefore, $x=1$ is a vertical asymptote.
Let $y=mx+c$ be an oblique asymptote of $H$.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
m & = & \dlim_{x\to \infty} \dfrac{f(x)}{x} \\
m & = & \dlim_{x\to \infty} \dfrac{x^2+3x}{x(x-1)} \\
m & = & \dlim_{x\to\infty} \dfrac{1+\frac{3}{x}}{1-\frac{1}{x}} \\
m & = & \dfrac{1+0}{1-0} \\
m & = & 1
\end{array}$$\begin{array}{rcl}
c & = & \dlim_{x \to\infty} \left[f(x)-mx\right] \\
c & = & \dlim_{x\to\infty} \dfrac{x^2+3x}{x-1}-x \\
c & = & \dlim_{x\to\infty} \dfrac{x^2+3x-x^2+x}{x-1} \\
c & = & \dlim_{x\to\infty} \dfrac{4x}{x-1} \\
c & = & \dlim_{x\to\infty} \dfrac{4}{1-\frac{1}{x}} \\
c & = & \dfrac{4}{1-0} \\
c & = & 4
\end{array}$Therefore, the oblique asymptote is $y=mx+4$.
-
$\begin{array}{rcl}
f(x) & = & \dfrac{x^2+3x}{x-1} \\
f'(x) & = & \dfrac{(x-1)(2x+3)-(x^2+3x)(1)}{(x-1)^2} \\
f'(x) & = & \dfrac{2x^2+x-3-x^2-3x}{(x-1)^2} \\
f'(x) & = & \dfrac{x^2-2x-3}{(x-1)^2} \\
f'(x) & = & \dfrac{(x+1)(x-3)}{(x-1)^2}
\end{array}$For the turning point(s),
$\begin{array}{rcl}
f'(x) & = & 0 \\
\dfrac{(x+1)(x-3)}{(x-1)^2} & = & 0 \\
(x+1)(x-3) & = & 0
\end{array}$$\therefore x=-1$ or $x=3$.
$\begin{array}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline
x & x< -1 & x=-1 & -1< x <1 & 1 < x <3 & x=3 & x>3 \\ \hline
f'(x) & +ve & 0 & -ve & -ve & 0 & +ve \\ \hline
f(x) & \text{increasing} & \text{max. point} & \text{decreasing} & \text{decreasing} & \text{min. point} & \text{increasing} \\ \hline
\end{array}$Therefore, the maximum point of $H$ is $(-1,1)$,
and the minimum point of $H$ is $(3,9)$.
-
- Consider the intersection points of $H$ and $y=10$, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\dfrac{x^2+3x}{x-1} & = & 10 \\
x^2+3x & = & 10x-10 \\
x^2-7x+10 & = & 0 \\
(x-2)(x-5) & = & 0
\end{array}$$\therefore x=2$ or $x=5$.
The required volume
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(\dfrac{x^2+3x}{x-1}-10\right)^2 dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(\dfrac{x^2-7x+10}{x-1} \right)^2 dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(\dfrac{x^2-7x+6+4}{x-1} \right)^2 dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(\dfrac{(x-6)(x-1)+4}{x-1} \right)^2 dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left( x-6+\dfrac{4}{x-1}\right)^2dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left( \dfrac{x^4+49x^2+100-14x^3+20x^2-140x}{x^2-2x+1}\right)dx \\
= & \pi\dint_2^5 \dfrac{x^4-14x^3+69x^2-140x+100}{x^2-2x+1}dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(x^2-12x+44+\dfrac{-40x+56}{x^2-2x+1}\right)dx \text{ , by long division.} \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(x^2-12x+44+\dfrac{-40x+40+16}{(x-1)^2}\right)dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(x^2-12x+44+\dfrac{-40(x-1)+16}{(x-1)^2}\right)dx \\
= & \pi \dint_2^5 \left(x^2-12x+44-\dfrac{40}{x-1}+\dfrac{16}{(x-1)^2}\right)dx \\
= & \pi\left[\dfrac{x^3}{3}-6x^2+44x-40\ln|x-1|-\dfrac{16}{x-1}\right]_2^5 \\
= & \pi \left(\dfrac{5^3}{3}-6(5)^2+44(5)-40\ln|5-1|-\dfrac{16}{5-1}-\dfrac{2^3}{3}+6(2)^2-44(2)+40\ln |2-1|+\dfrac{16}{2-1}\right) \\
= & \pi(57-40\ln 2^2) \\
= & \pi(57-80\ln 2)
\end{array}$
2022-M2-09
Ans: (a) $x=1$, $y=x+4$ (b) max point: $(-1,1)$, min point: $(3,9)$ (d) $\pi[57-80\ln 2]$

