- Sketch the graph according to the question.
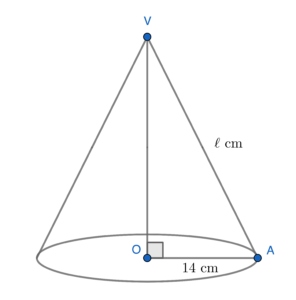
Let $\ell \text{ cm}$ be the slant height of the cone. Then we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\pi (14)(\ell) & = & 700\pi \\
\ell & = & 50
\end{array}$Therefore, the slant height of the cone is $50\text{ cm}$.
The height of the cone
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \sqrt{50^2 -14^2} \\
= & 48\text{ cm}
\end{array}$ -
- Sketch the graph according to the question.
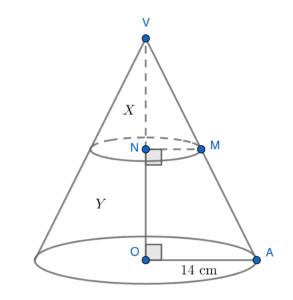
The volume of the original cone
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & \dfrac{1}{3} \pi(14)^2(48) \\
= & 3136\pi \text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$The surface area of $X$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 700\pi \times \dfrac{1}{1+15} \\
= & \dfrac{175}{4}\pi\text{ cm}^2
\end{array}$Since $X$ and the original cone are similar to each other, we have
$\begin{array}{rcl}
\left(\dfrac{\text{volume of the original cone}}{\text{volume of $X$}}\right)^2 & = & \left(\dfrac{\text{curved surface area of the original cone}}{\text{curved surface area of $X$}}\right)^3 \\
\left( \dfrac{3136\pi}{\text{volume of $X$}}\right)^2 & = & \left( \dfrac{700\pi}{\frac{175}{4}\pi}\right)^3 \\
\text{volume of $X$} & = & 49\pi \text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$Hence, the volume of $Y$
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 3136\pi -49\pi \\
= & 3087\pi\text{ cm}^3
\end{array}$ - Let $r\text{ cm}$ be the radii of the spheres.
$\begin{array}{rcl}
2 \times \dfrac{4}{3} \pi r^3 & = & 3087\pi \\
r^3 & = & \dfrac{9261}{8} \\
r & = & \dfrac{21}{2}
\end{array}$Hence, the diameter of the spheres
$\begin{array}{cl}
= & 2 \times \dfrac{21}{2} \\
= & 21\text{ cm}
\end{array}$
- Sketch the graph according to the question.
2023-I-14
Ans: (a) $48\text{ cm}$ (b) (i) $3087\pi\text{ cm}^3$ (ii) $21\text{ cm}$

