- Equal arcs imply the angles at the centre equal.
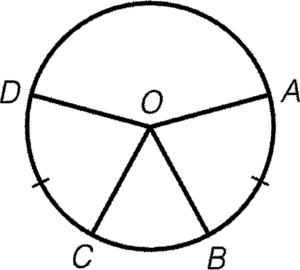
Condition: $\overparen{AB}=\overparen{CD}$
Result: $\angle AOB = \angle COD$
Reference: eq. arcs, eq. $\angle$s
- Equal angles at centre imply the corresponding arcs equal in length.
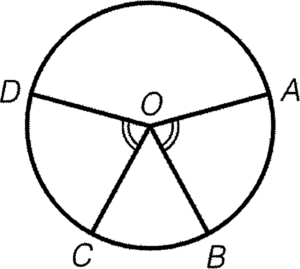
Condition: $\angle AOB = \angle COD$
Result: $\overparen{AB} = \overparen{CD}$
Reference: eq. $\angle$s, eq. arcs
- Equal chords imply equal angles at the centre.
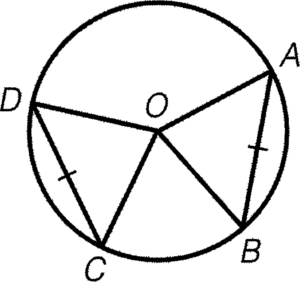
Condition: $AB=CD$
Result: $\angle AOB= \angle COD$
Reference: eq. chords, eq. $\angle$s
- Equal angles at centre imply the corresponding chords equal in length.
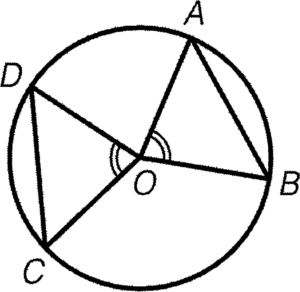
Condition: $\angle AOB=\angle COD$
Result: $AB=CD$
Reference: eq. $\angle$s, eq. chords
- Equal chords imply the corresponding arcs equal in length.
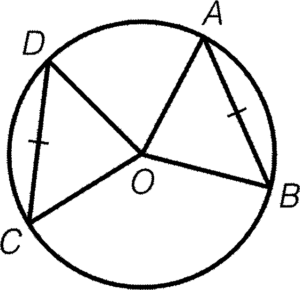
Condition: $AB=CD$
Result: $\overparen{AB}=\overparen{CD}$
Reference: eq. chords, eq. arcs
- Equal arcs imply the corresponding chords equal in length.
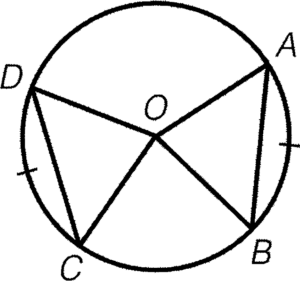
Condition: $\overparen{AB}=\overparen{CD}$
Result: $AB=CD$
Reference: eq. arcs, eq. chords
- The lengths of arcs are proportional to the sizes of the angles at centre.
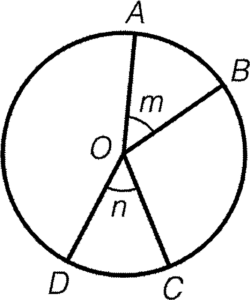
Result: $\overparen{AB}:\overparen{CD}=m:n$
Reference: arc and $\angle$ at centre in prop.

