- The angle at centre is twice the corresponding angle at circumference.

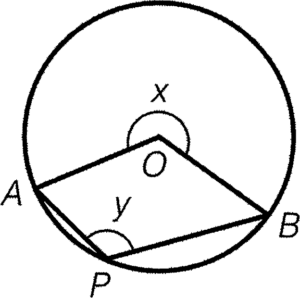
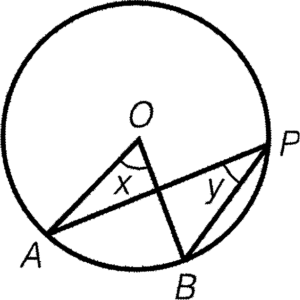
Result: $x=2y$
Reference: $\angle$ at centre twice $\angle$ at circumference
- If $AB$ is a diameter of the circle and $P$ is a point of the circumference, then $\angle APB$ is a right angle.
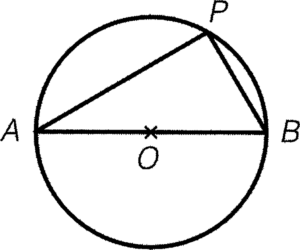
Condition: $AB$ is a diameter
Result: $\angle APB=90^\circ$
Reference: $\angle$ in semi-circle
- If $\angle APB$ is a right angle, then $AB$ is a diameter of the circle.
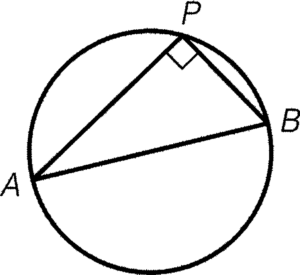
Condition: $\angle APB=90^\circ$
Result: $AB$ is a diameter of the circle
Reference: converse of $\angle$ in semi-circle
- All angles in the same segment are equal.

Result: $x=y$
Reference: $\angle$s in the same segment
- If $\angle ADB$ and $\angle ACB$ equal, then $A$, $B$, $C$ and $D$ are concyclic.
Condition: $\angle ADB=\angle ACB$
Result: $A$, $B$, $C$ and $D$ are concyclic.
Reference: converse of $\angle$s in the same segment
- The ratio of two angles at circumference equals to the ratio of the length of the corresponding arcs.

Result: $\overparen{AB}:\overparen{CD} = x:y$
Reference: arcs and $\angle$s at circumference in prop.

