- If $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle at $T$, then $OT$ is perpendicular to $PQ$.
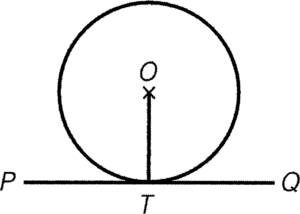
Condition: $PQ$ is a tangent at $T$
Result: $OT \perp PQ$
Reference: tangent $\perp$ radius
- If $OT$ is perpendicular to $PTQ$, then $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle at $T$.
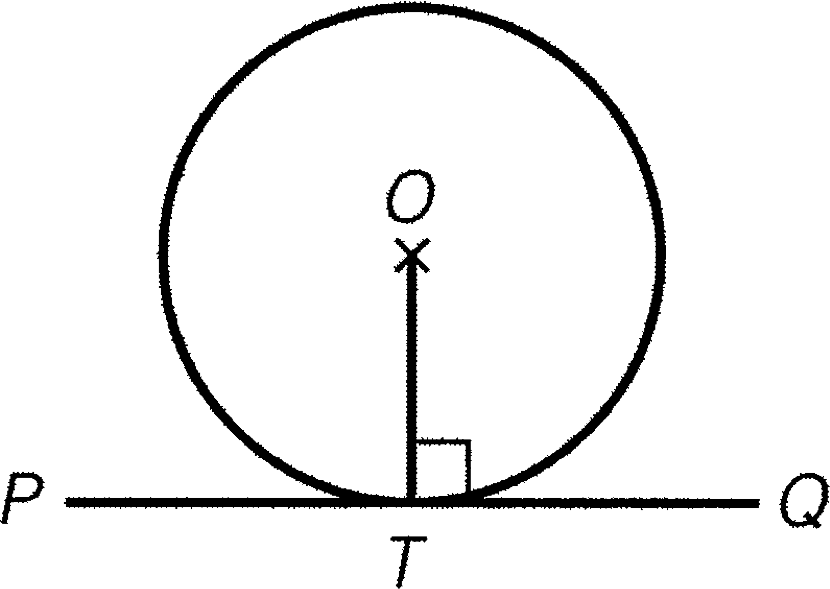
Condition: $OT\perp PTQ$
Result: $PQ$ is a tangent
Reference: converse of tangent $\perp$ radius
- If $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle at $T$, any straight line perpendicular to $PQ$ and passing through $T$ must pass through the centre.
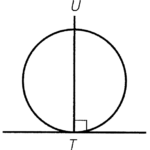
Condition: $PQ$ is a tangent at $T$ and a perpendicular line passing through $T$
Result: The straight line must pass through the centre
Reference: line passing through the pt of contact $\perp$ tangent passes through centre
- Given that $PT$ and $QT$ are two tangents to the same circle. Then $\Delta OPT \cong \Delta OQT$.
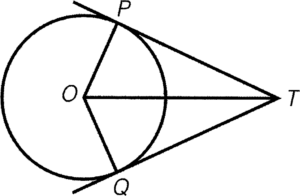
Condition: Two tangents $PT$ and $QT$
Result:
- $PT=QT$
- $\angle PTO=\angle QTO$
- $\angle TOP = \angle TOQ$
Reference: tangent properties
- If $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle, then the angles in alternate segment equal.
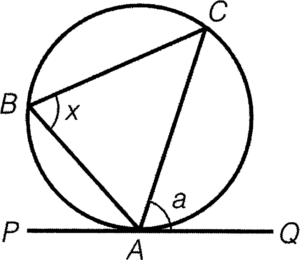
Condition: $PQ$ is a tangent
Result: $\angle ABC = \angle CAQ$
Reference: $\angle$ in alt. segment
- If the angles in the alternate segment equal, then $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle at $A$.

Condition: $\angle ABC=\angle CAQ$
Result: $PQ$ is a tangent to the circle
Reference: converse of $\angle$ in alt. segment

